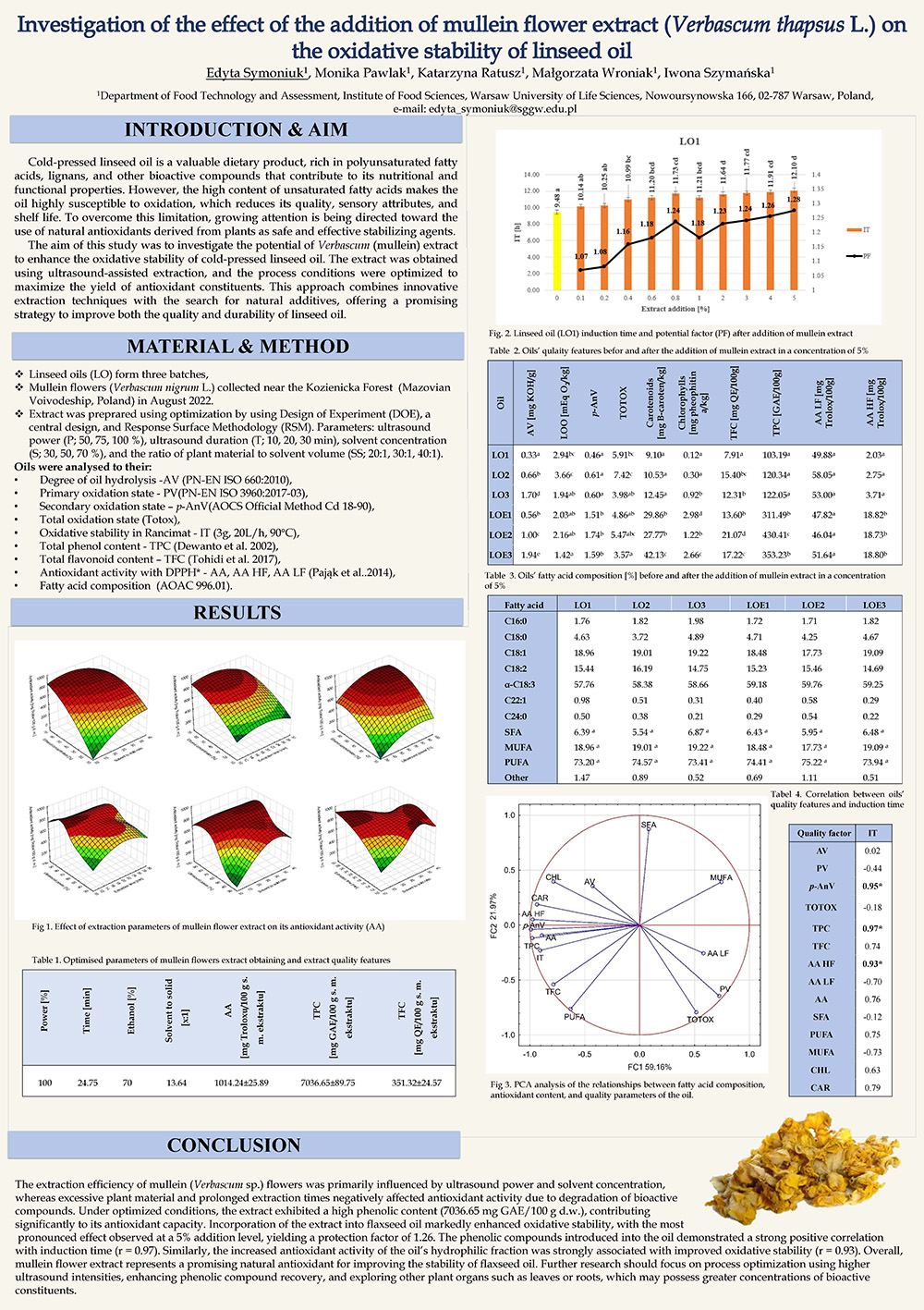
Vegetable fats are recognized for their health-promoting properties. Among them, linseed oil is distinguished by its exceptionally high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids and a particularly favorable n-3 to n-6 fatty acid ratio. More than 70% of its total fatty acid profile is composed of unsaturated fatty acids. Although this composition underlies many of its beneficial health effects, it also renders the oil highly susceptible to oxidative degradation, thereby limiting its shelf life. The incorporation of bioactive compounds with antioxidant activity presents a promising strategy to improve the oxidative stability of linseed oil. While synthetic antioxidants are routinely employed for this purpose, growing evidence of their potential adverse effects on human health has intensified interest in natural alternatives with strong antioxidative potential. Mullein flowers (Verbascum L.) constitute a particularly rich source of such compounds, including iridoids and iridoid glycosides, flavonoids, saponins, phytosterols, terpenes, phenolic acids, and carotenoids.
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of mullein flower extract on the oxidative stability of linseed oil. The theoretical part discussed the composition, properties, and applications of linseed oil and mullein. The lipid oxidation process and techniques for enriching oils with antioxidant compounds, including the use of ultrasound, were described. In the experimental part, the ultrasound-assisted extraction of antioxidant compounds from mullein flowers was optimized, with antioxidant activity (AA) used as the optimization parameter. The optimized extract was added to linseed oil, determining the optimal addition level at 5%. Both fresh linseed oil and the oil enriched with the extract were subjected to safety analysis, and their oxidative stability and bioactive compound content were determined. The results confirmed the effectiveness of mullein extract as a natural antioxidant, with linseed oil stability increasing on average by 26%. Moreover, the oil with the extract showed a higher degree of hydrolysis and a higher level of secondary oxidation products. The addition of the extract increased the content of bioactive compounds in linseed oil, especially phenolics, which increased threefold to values ranging from 311.49 to 430.41 mg GAE/100 g of oil. The induction time of the oil was strongly positively correlated with the phenolic content (r = 0.97), anisidine value (r = 0.95), and antioxidant activity of the oil’s hydrophilic fraction (r = 0.93).
Keywords: mullein, linseed oil, ultrasound-assisted extraction, oxidative stability